 Unit three: Botany
Unit three: Botany
Botany is the study of
plants. There more than 300,000 species of plants globally estimated by botanists[1]. And
about 6,600 of these plant species are found Ethiopia[2].
The hierarchical level of organization in plants
follows that of animals. Plant cells that
have similar characteristics/or functions/ come together to form plant tissues. Then
plant tissues form five distinct structures (the equivalent of organs in animals). Structures are groups of plant tissues working together with
a common function (e.g., roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds). The different plant structures form two plant
systems (the equivalent of organ systems in animals) namely: root and shoot
system. Therefore, a plant is made up of a number of coordinated structures to
form a working unit (a plant in this case).
In this unit you will be
introduced into the basics of organization and structure of plants. Furthermore,
basic terms and processes are dealt here along with a brief introduction to the
taxonomy(see Figure.1). The detailed taxonomy of plant kingdom is dealt in book 4.
3.1. Taxonomy of plants
Figure.1 Chart showing traditional plant taxonomy
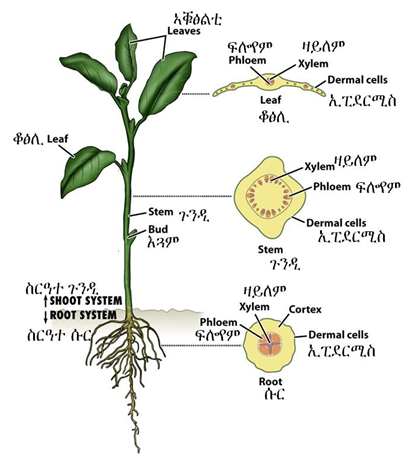
3.2. Level of organization in plants
Figure 3. 1. General morphology of plants
Figure 3. 2. Parts of plant
3.3. Vegetables…………………….….
ኣሕምልቲ
Vegetables (ኣሕምልቲ) are plants used as foodstuffs. A
simple way to classify vegetables is to group them according to their edible
parts (i.e which part of them is edible). Thus, vegetables includes: bulbs [ሽጉርቶ], fruit [ፍረ], tuber [ዓካር] and rhizome [ራይዞም][1].
1. Legumes [leguminous] ጥረኣዊ [ጥራምረ]
The main edible part of these groups of pod-shaped
fruits[2]
is their seeds, consumed fresh, dried and/or sprouted.
2. Fruits [ፍራምረ]
Fruits are sually sweet vegetables. The main
edible part of these vegetables is their bulb like
Onion (ሽጉርቶ: ሽጉርቲ መሰል ሱር ዘለዎም ኣትክልቲ), Rhizome
(like potatoe, sugar beet) the where the plant’s nutrient reserves are stored
in an underground structure.
[2] (ለቖታ ከም ናይ ዓይኒ ዓተር) and ; if dried, they often require soaking before they can be
cooked. primarily consumed at breakfast, as a snack or for dessert, and used
extensively in pastry and candy making




No comments:
Post a Comment